
Renewable Energy Manufacturing: Opportunities for Southeast Asia
This report presents an assessment of Southeast Asia to become a leader in renewable energy manufacturing. It also identifies key opportunities for intraregional collaboration.
Greater Mekong Subregion countries are in varying stages of economic development but share common goals concerning energy security and environmental protection. Progress have been made in promoting renewable energy, clean fuels, and energy efficiency, but new energy solutions remain crucial to the subregion’s advancement.
The GMS Economic Cooperation Program Strategic Framework 2030 (GMS-2030) emphasizes cross-border power trade, establishment of regional grid codes, development of regional markets, and expanding clean energy investments with a greater role for the private sector.
The Regional Power Trade Coordination Committee (RPTCC) managed regional power trade in the subregion from 2004–2022. In July 2022, at the 29th RPTCC meeting, the committee formally transitioned to the GMS Energy Transition Taskforce (ETTF). Among other things, the transition to ETTF ushers in closer energy cooperation with the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and its initiatives, such as the ASEAN Power Grid.
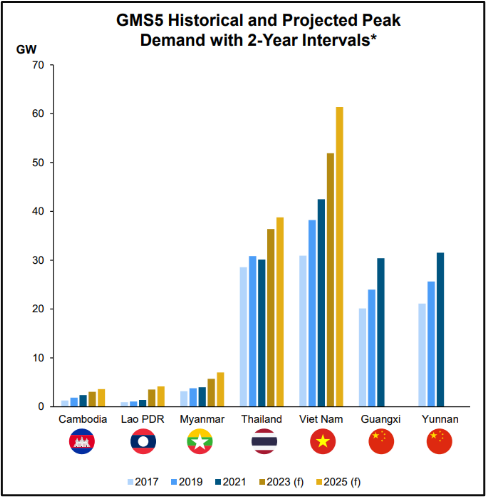
Energy consumption in the GMS countries has grown intensively as their economies develop, driven mostly by residential and industrial sectors. Demand is forecasted to increase materially over the medium term.
GMS countries have used different approaches to increase access to reliable, affordable, and low-carbon energy.
See initiatives of the GMS Energy Transition Task Force to promote energy security in the subregion in a sustainable manner.
Related
Key Energy Resources
Focal Persons at the Asian Development Bank
Hyunjung Lee (lead)
Energy Sector Office
Sectors Group
Atsumasa Sakai
Energy Sector Office
Sectors Group
Other Concerned Staff & Consultants
Joao Aleluia
Energy Sector Office
Sectors Group
Architrandi Priambodo
Energy Sector Office
Sectors Group
Jeffrey Almera
Energy Sector Office
Sectors Group
Pinsuda Alexander
Regional Cooperation and Integration Unit
Southeast Asia Department
Rafaelita Jamon
Regional Cooperation and Integration Unit
Southeast Asia Department/GMS Secretariat
Send inquiries to GMS Secretariat.

This report presents an assessment of Southeast Asia to become a leader in renewable energy manufacturing. It also identifies key opportunities for intraregional collaboration.
Despite welcome progress on universal access to electricity, the transition to renewable energy is faltering at a time when multiple shocks are hitting Asia and the Pacific hard.
Greater Mekong Subregion countries will meet on 13-14 June 2023, Manila, Philippines, for the first GMS Energy Transition Task Force Meeting (ETTF).
The Asian Economic Integration Report 2023 highlights the continued growth of integration in subregional initiatives and programs in Southeast Asia, including both in the GMS and the ASEAN, from 2006 to 2020.
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) today joined the Global Energy Alliance for People and Planet (GEAPP) to announce $35 million to help boost energy access and the energy transition in South and Southeast Asia.

This report explains the complex challenges facing the six countries in the renewables-rich Greater Mekong Subregion (GMS) as they work to implement a comprehensive framework to enable regional electricity power trading.

This document presents progress made and achievements from January to December 2022 of the ASEAN Catalytic Green Finance Facility (ACGF).
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) has approved a sector development program that combines a $50 million policy-based loan package with $23 million in project investments to support the energy transition of Cambodia. The Energy Transition Sector Development Program includes ADB’s first comprehensive policy reform package for the energy sector in Cambodia.
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) and Monsoon Wind Power Company Limited (Monsoon) signed a $ 692.55 million nonrecourse project financing package to build a 600-megawatt wind power plant in Sekong and Attapeu provinces in the southern region of the Lao People’s Democratic Republic (Lao PDR) to export and sell power to neighboring Viet Nam. Comprising 133 wind turbines, the project will be the largest wind power plant in Southeast Asia and the first in the Lao PDR.
A partnership between the Asian Development Bank (ADB) and Electricite du Cambodge (EDC), Cambodia’s national power utility, to develop a 100-megawatt (MW) National Solar Park reached a milestone with the park’s first 60 MW solar photovoltaic (PV) power generation plant connecting to the national grid. ADB President Masatsugu Asakawa marked the occasion with a visit to the solar park on 11 November, during which he initiated the start of power delivery.